Step 3
You can access the server's header attributes from the request object (req). For example, update the route handler for /api/users and add the following snippet as the handler's first job!
const { authorization } = req.headers;
console.log(authorization);
Save the file and run the server. Then, using Postman, send a request to access /api/users and enclose the authorization token. The token must be printed to the console when the server receives this request:

Notice the authorization includes the "Bearer" keyword!
Let's use the token to authorize a user: If the user has a valid token and an "admin" role, we allow them to see the list of users. Otherwise, we will respond with 403 (Forbidden).
First, add the following function to server/util/token.js:
const decodeToken = (token) => {
const decoded = jwt.decode(token);
return decoded;
}
Make sure to export it:
module.exports = {
createToken,
verifyToken,
+ decodeToken
};
Next, add the following import to server/routes/users.js:
const { verifyToken, decodeToken } = require("../util/token");
Finally, update the route handler for /api/users and add the following snippet!
const { authorization } = req.headers;
const [_, token] = authorization.trim().split(" ");
const valid = await verifyToken(token);
const user = decodeToken(token);
if (!valid || user.role !== "ADMIN") {
return res.status(403).json({
message:
"You are not authorized to access this resource.",
});
}
Save the changes. Then, using Postman, send a request to access /api/users and enclose the authorization token of a regular client(rather than an admin).
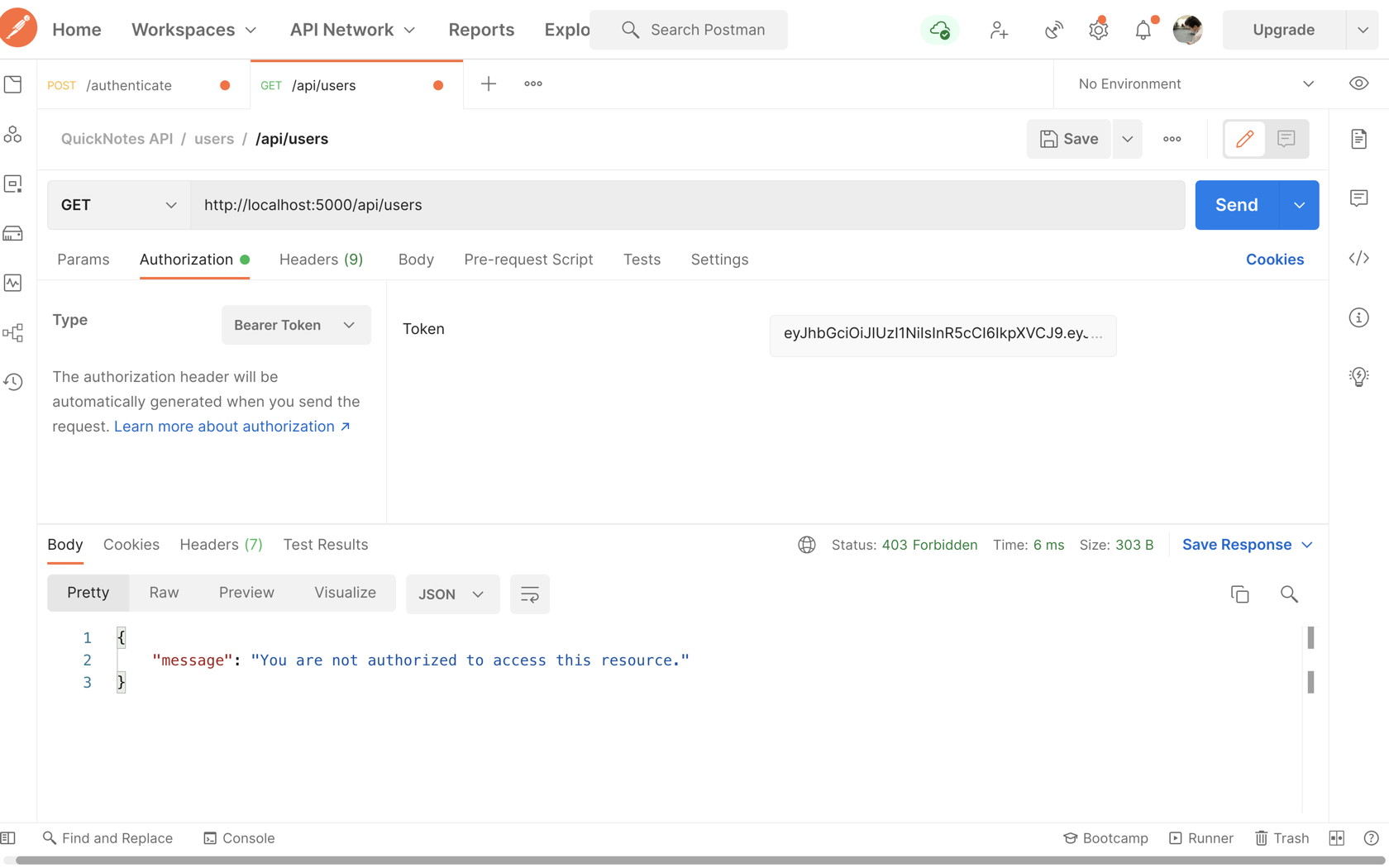
Notice the server responded with 403: Access forbidden!